Clinic Services
- Clinical examination
- Local and international online statements
- Supervision of private hospital cases in Cairo and Giza

Cervical, thoracic or lumbar disc herniation
A herniated disc in the lumbar or cervical spine is a condition in which the soft, gel-like center of the disc between the vertebrae pushes outward through a tear in the outer layer of the disc. This can put pressure on the nerves that run through the spine, causing pain, numbness, and tingling.

Neck pain and lower back pain
Neck and lower back pain are among the most common types of pain experienced by people of all ages. Neck pain can range from a dull ache to a severe throbbing pain. It can be localized in the neck area or radiate to the shoulders, arms, and head. Lower back pain can also range from mild to severe. It can be localized in the lower back area or radiate to the buttocks, legs, and feet.

Trigeminal nerve pain in the face
The trigeminal nerve, also known as the fifth nerve, is the largest and most complex of the twelve cranial nerves. It is a mixed nerve, meaning it carries both sensory and motor information. The trigeminal nerve is responsible for sensation in the face, mouth, and teeth, and for movement of the muscles of mastication (chewing).
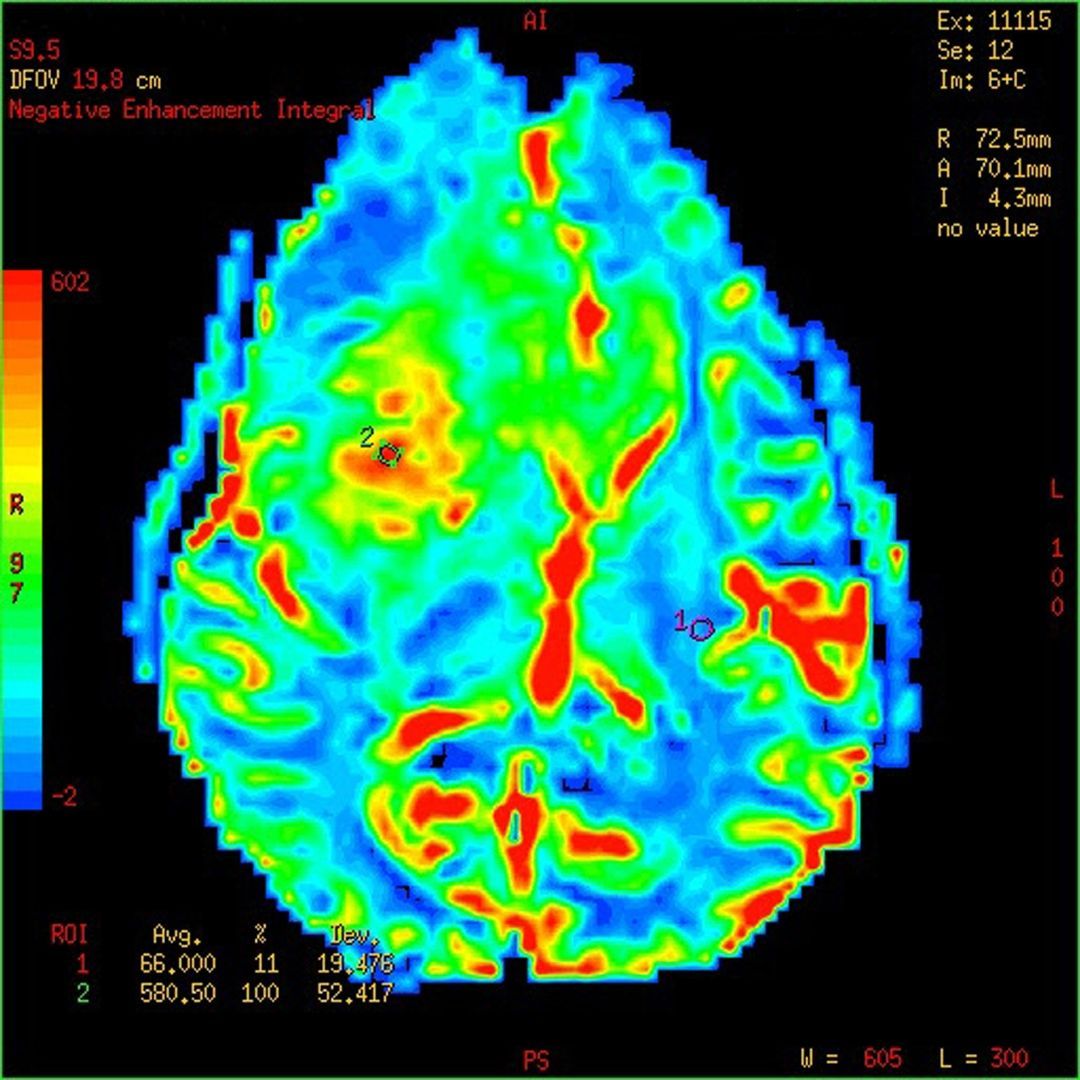
Primary and secondary malignant brain tumors
Primary brain tumors are tumors that begin in brain cells. These tumors arise from a variety of cells, including glial cells, which support nerve cells, and the nerve cells themselves. Secondary brain tumors are tumors that spread from another part
of the body to the brain. Any type of cancer can spread to the brain, but some of the most common types include lung cancer, breast cancer, prostate cancer, and skin cancer.
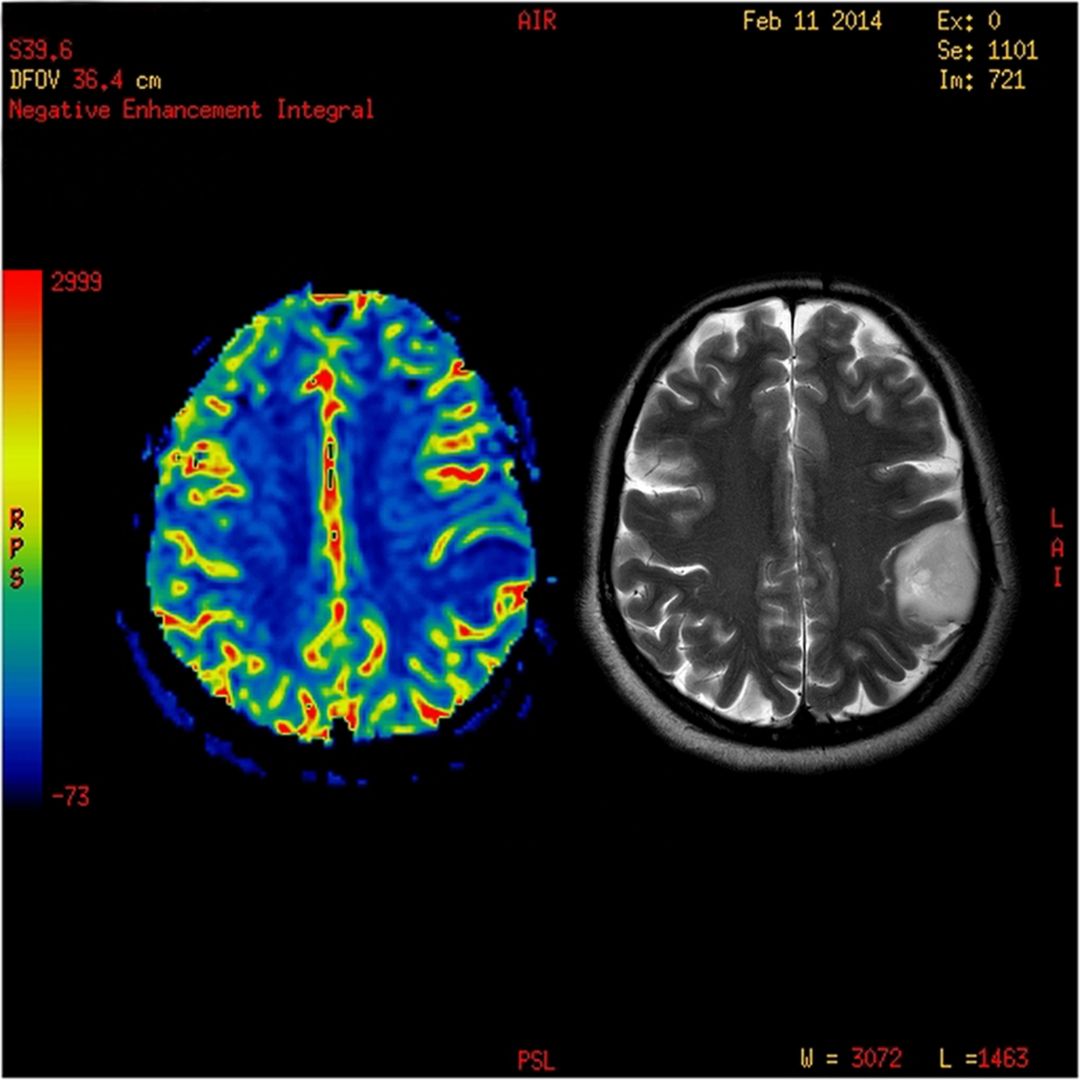
Benign brain tumors
A benign brain tumor is a noncancerous growth in the brain that does not spread to other parts of the body. Benign brain tumors are the most common type of brain tumor, accounting for about 70% of all brain tumors. Benign brain tumors can occur anywhere in the brain, but are most common in the frontal lobe, parietal lobe, and temporal lobe.


